
Table of Contents
It’s not the first time we’ve chatted with a chatbot. Why has ChatGPT captured 100 million users in just two months? And why have well-known companies like JP Morgan put a strict ban on it? This article will introduce ChatGPT and its consequent information security issues. Last but not least, we also include the status quo of Taiwanese companies to help you avoid the trap of this AI frenzy.
ChatGPT is an AI language model created by OpenAI that uses deep learning to understand and generate natural language and can communicate with users. In other words, it uses machine learning to create specifically text-based works, while generative AI, in general, can create works in more forms of images and videos, etc.
Technically, it’s based on GPT-3 technology and incorporates reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to make it more like a human in conversation. You can imagine that it was trained by absorbing human compliments or corrections, further adjusting its words to generate natural-sounding responses.
In addition, developers also adjusted to ensure safety and ethics before ChatGPT’s official launch.
Due to the popularity of ChatGPT, Microsoft and Google have successively launched their own generative AI models. At the same time, chip companies such as AMD and Nvidia have also raced to cash in AI. It might amaze you that, according to a survey of 1,000 companies by Resumebuilder, nearly half of them have introduced generative AI models like ChatGPT to optimize labor workflow. After improving the inefficiency of manual operations, enterprises can also create higher profits.
Chatbot has been introduced into the business for a long time, such as intelligent customer service, intelligent search, and automatic translation. However, they mainly relied on rule-based responses, which are limited and less personalized. But now, with the help of GPT-3, businesses can use chatbots more flexibly; the quality and customer experience will improve accordingly.
One example is the Japanese company “Bengoshi.com,” which mainly provides legal consultation services. Unlike traditional one-on-one consultations, which are labor-intensive and inefficient, the company will soon offer online consultations using ChatGPT technology. Because of the local law, this AI service will be free of charge. The emergence of this new AI business model also led to a 6% increase in the company’s stock price the next day.
But, while ChatGPT has sparked an investment boom and business model innovation, companies such as JP Morgan, Verizon, and Walmart have turned it away and strictly prohibited their employees from using AI models like ChatGPT.
PwC: Nearly 30% of companies suffer losses of $1 to $20 million due to data leakage.
Those renowned companies are not stupid. Even AI models like ChatGPT explicitly emphasize their security, but hackers still find ways to breach security measures. We will explore two potential ways where ChatGPT might contribute to the cybersecurity risk:
AI digital transformation is secretly taking place despite no outbreak of information security regarding ChatGPT now. Security issues will be a critical concern for businesses to pay attention to. So now, let’s bring the focus back to Taiwanese listed companies; how is their security performance?
According to the TEJ ESG Radar, information security incidents have increased significantly since the pandemic. As of February this year, five security incidents have occurred, including serious issues such as customer information leaks. The following are summaries of recent incidents, including 3 events regarding data leaks:
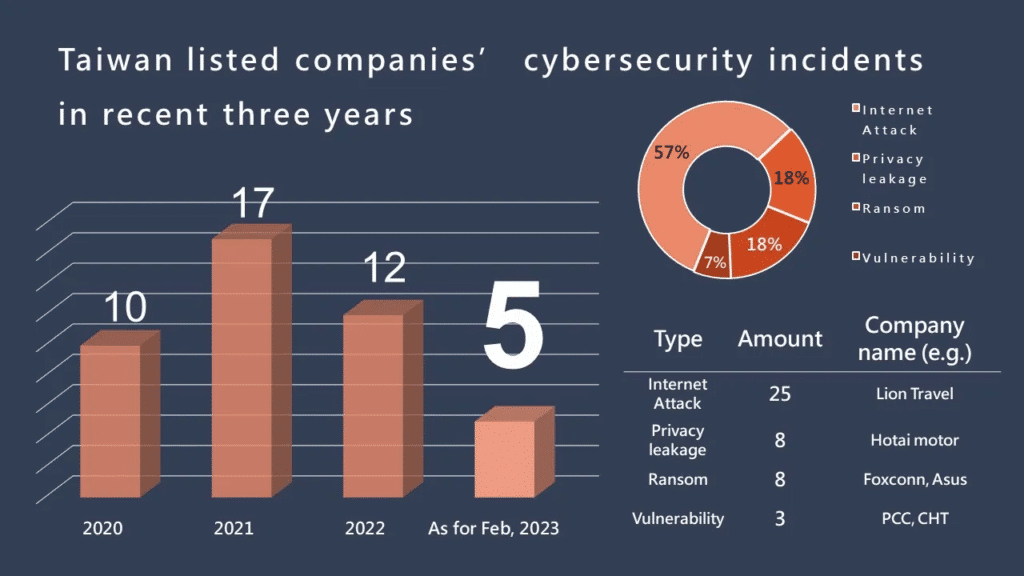
AI technology not only accelerates digital transformation but also puts companies at a security risk. Since most companies have not disclosed detailed information on the subsequent impact, nearly 60% of incidents are only summarized as “ Internet/ Hacker attacks.” Therefore, it’s necessary for further transparency in corporate security disclosures. In the following article, we will tell you how to view a company’s engagement in information security from its “Information Security Pass.”
Follow the recent information security issue of Taiwanese companies through TEJ ESG Radar…
If you have any questions about this article or would like to obtain further access to the TEJ database, please feel free to leave a comment, call, or mail us.
About us
⭐️ TEJ Website
⭐️ LinkedIn
✉️ E-mail: finasia@tej.com.tw
☎️ Phone: 02–87681088