
Table of Contents
ESG is a concept proposed by the United Nations Global Compact in 2004. ESG in Chinese refers to “environmental”, “social” and “governance.” These three pillars are essential indicators for evaluating the sustainable operation of enterprises. The following explains the meaning of ESG:
E – Environmental:
It represents the need for enterprises to pay attention to the impact and responsibility of environmental sustainability issues during their operations and development processes, including reducing carbon emissions, climate change, energy conservation, pollution management, etc. It is used to measure whether enterprises have considered the environment’s maintenance during development.
S – Social:
It means that enterprises must pay attention to relevant social issues in the process of operation and development and fulfill their responsibilities to society. This includes how companies manage employees, consumers, or employee rights, corporate working environment, support for charity, labor human rights, social participation, etc., to promote companies’ establishment of a good workplace environment and implementation of corporate social responsibilities.
G – Governance:
It refers to the transparency, responsibility, efficiency, and fairness of various matters in the company’s management and operation process. It includes topics such as company senior management, executive compensation, shareholder rights, information transparency, risk management, board governance, supply chain management, etc. It is used to evaluate a company’s managers and operations. Combining these three ESG concepts can determine how a company can contribute to sustainable development while making profits.
ESG is an essential indicator for evaluating the sustainable development of a company and is also one of the critical issues that investors pay attention to. When the financial crisis broke out, companies with higher ESG scores were less affected because of their long-term investment in social assets, making ESG more critical. Although business operations need to pay attention to financial data, if they take actions that harm the environment or infringe on consumer rights for the sake of revenue results, it will affect the company’s reputation. Moreover, as the problem of climate change intensifies, environmental risks are an issue that the world must pay attention to. Therefore, both investors and social groups have begun to supervise the response measures of enterprises or governments to environmental risks.
In other words, ESG risks have become one of the critical factors affecting corporate finance and reputation. For example, environmental and social violations have caused the company to be fined or face legal risks such as lawsuits, or there have been disputes about ethical flaws in its operating methods, and the media have criticized it. Damage to brand reputation caused by reports. Therefore, there are five benefits for companies to implement ESG:
This article will select the top 4 popular ESG ETFs in the market as investment targets:
This article uses Windows 11 and VS code as the editor.
import os
import pandas as pd
tej_key = 'your key'
api_base = 'https://api.tej.com.tw'
os.environ['TEJAPI_KEY'] = tej_key
os.environ['TEJAPI_BASE'] = api_base
start = '2018-01-01'
end = '2023-12-31'
stock_list = ['00692', '00850', '00878', '00888', 'IR0001']
calendar_name = 'TEJ'
os.environ['mdate'] = start + ' ' + end
os.environ['ticker'] = ' '.join(stock_list)
!zipline ingest -b tquantNext, we are going to build the backtest environment. First, we could collect multiple targets’ quantitative indicators and price and volume data. In this case, we used it to obtain data on four ESG ETFs, which can avoid processing stocks that have yet to be listed.
This section is to define the daily trading environment before the start of trading. In this example, we set the following conditions:
The function below is essential for building a trading strategy. It will be called every day after the backtest starts. The main task of this article is to set an order equal to 25% of the current value of the investment portfolio.
def handle_data(context, data):
out_dir = pipeline_output('mystrats')
for asset in out_dir.index:
stock_position = context.portfolio.positions[asset].amount
if stock_position == 0:
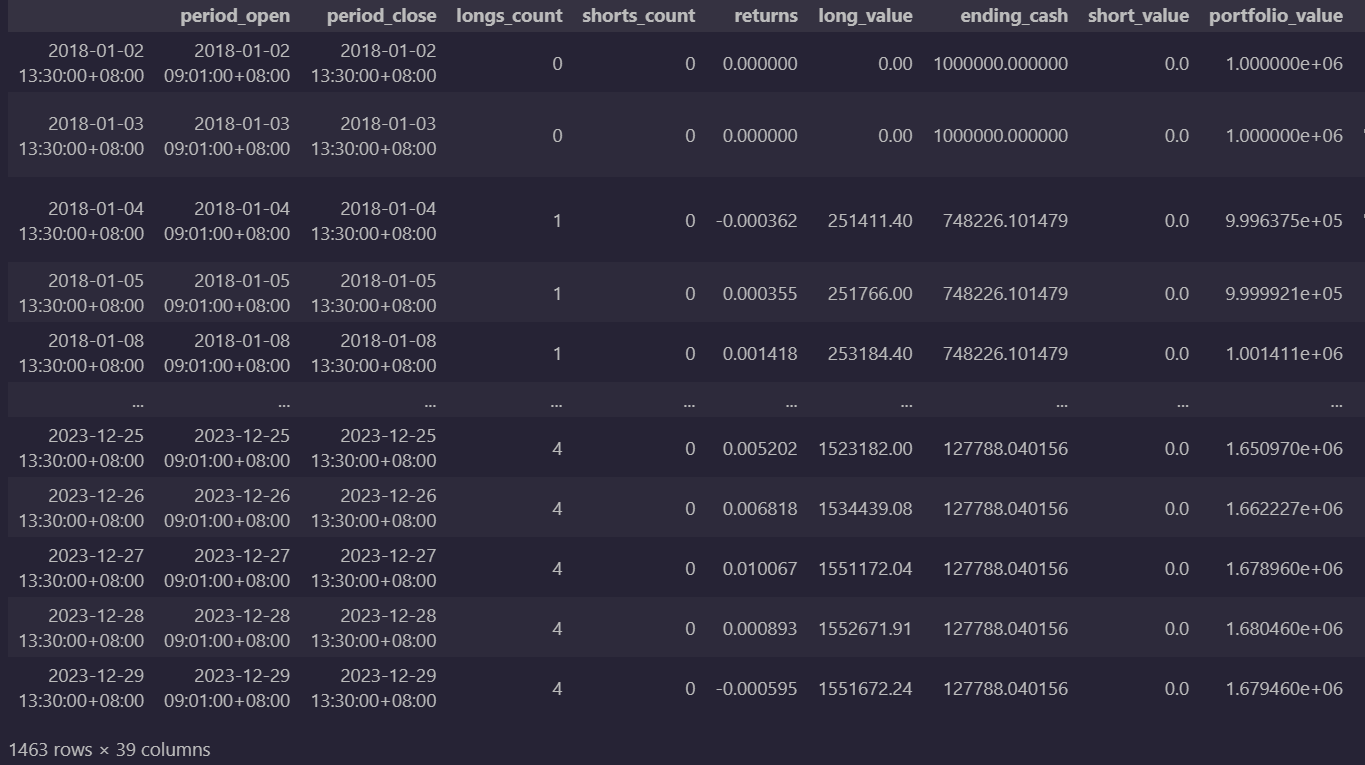
order_percent(asset, 0.25)Next, we can start carrying out our trading strategy. Based on the set above, we execute the buy-and-hold the ESG ETFs. Set the trading period from start_date (2018-01-01) to end_date (2023-12-31)and used the data we collected earlier. The initial capital for the trading strategy is $1,000,000. The output results are a detailed list of daily performance and transactions.
To further understand the performance of this strategy, we compared the cumulative returns of this strategy with the cumulative return of the benchmark index and visualized the results as follows:
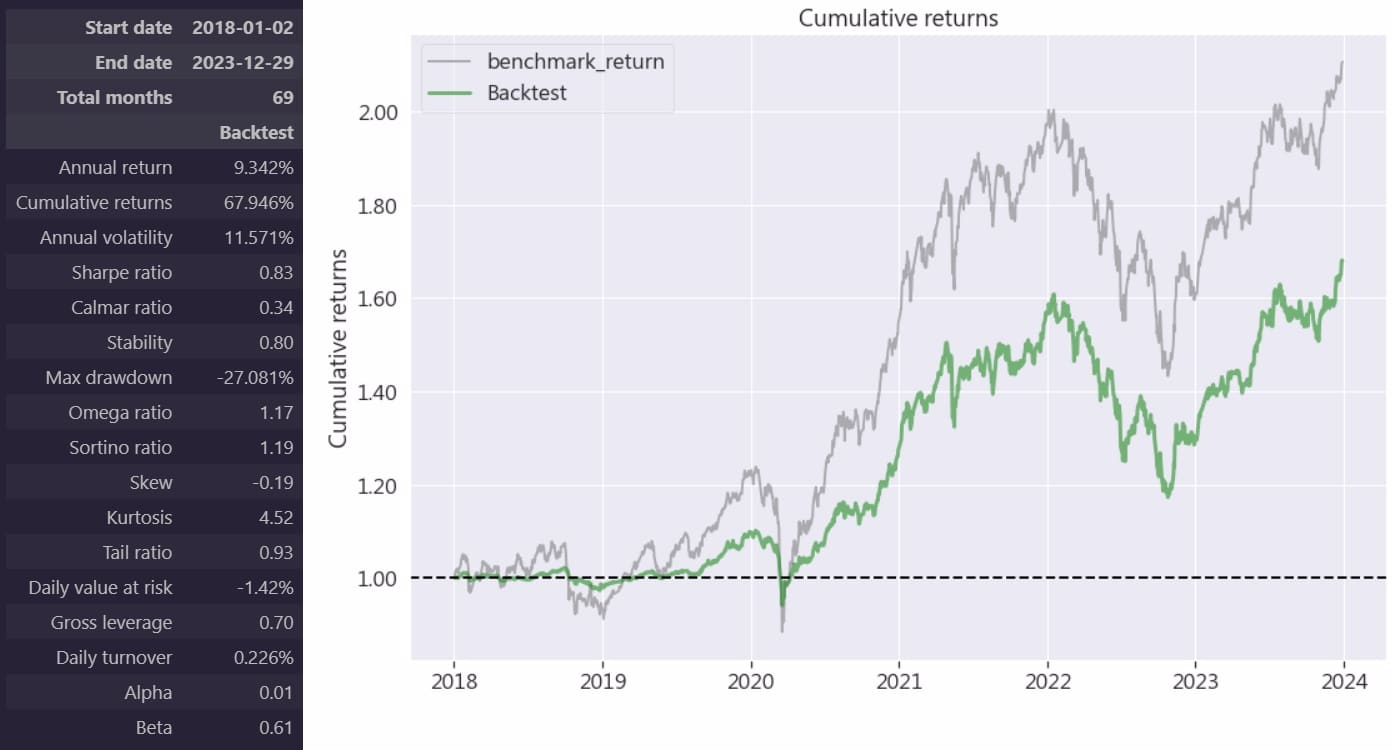
From the chart above, we can see that the market has a return of 2 times in these 5 years, while the return of buying and holding ESG ETFs is slightly lower, but it still has a cumulative return of more than 1.6 times. In addition, we also see that the fluctuations of the ESG ETF investment group are almost consistent with the broader market, but the annualized volatility and maximum drawdown are 11.57% and -27.08% respectively. This fluctuation range is relatively small compared to the broader market. Moreover, a Beta value < 1 means that this investment portfolio is not sensitive to changes in the overall market. Various indicators show that ESG ETFs are making stable profits at lower risks, reflecting the three major aspects of the ESG concept:
In this implementation, we selected four ESG ETFs as investment targets to conduct a backtest performance analysis of buy-and-hold targets. The backtest results of this four-tier ESG ETF performed well in cumulative and annualized returns, reaching 67.95% and 9.34%, respectively. The annualized volatility and maximum drawdown were 11.57% and -27.08%, respectively. This shows that ESG ETFs have achieved solid returns and controlled risks. The beta value shows that the performance relative to the broader market is relatively stable and less affected by market fluctuations. However, it can be seen from the Sharpe Ratio and Alpha that ESG ETFs have less excess returns, reflecting that the ESG corporate industry attaches great importance to the stability of various company indicators.
Overall, these factors make ESG ETFs stable in performance and less volatile. Investing in ESG ETFs is better for obtaining long-term stable growth than short-term swing returns.
Learn More About the High-Quality ETF Database by TEJ!
Construct Trading Strategies With Market Data.