
With the vigorous development of big data applications and cloud computing, Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) are actively constructing data centers, driving growth in the server market. Especially after OpenAI launched ChatGPT, opportunities in the GenAI sector have flourished, sparking a wave of AI infrastructure development. AI servers, in particular, have seen significant hardware improvements compared to normal servers, even adopting new technologies that increase integration and testing complexity. Some assembly factories, leveraging their technical expertise, have successfully tapped into the AI boom, opening up a new growth opportunity for the EMS industry.
Table of Contents
Generally speaking, the assembly industry refers to the EMS industry, encompassing the manufacturing and assembly of electronic products, such as smartphones, laptops, automotive electronics, and servers. EMS companies in Taiwan include Quanta (2382.TW), Wistron (3231.TW), PEGATRON (4938.TW), Compal (2324.TW), Inventec (2356.TW), and the world’s biggest EMS company — Foxconn (2317.TW).
Common assembly can be divided into the followings,
| Full form | Characteristics | |
| OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer | OEM companies manufacture products based on customer’s requirements and designs, and brand their logo on the product. Profit arises from production and producing only. |
| ODM | Original Design Manufacturer | Aside from producing capability, ODM companies also posses the ability to design and develop. Through customizing products, ODM companies usually have higher bargaining power with customers. |
| OBM | Original Brand Manufacturer | OBM companies not only own the brand but also have the ability to develop, design, manufacture, and sell. |
| EMS | Electronics Manufacturing Services | EMS companies provide full service from design to manufacture. Moreover, EMS companies also have the professional knowledge in supply chain, offering services including Inventory Management, Transportation, and Repairment. |
Servers are specialized enterprise-grade computers designed to process and store large amounts of data. It is commonly used to run applications or provide services. Clients and employees can connect to servers via mobile devices or personal computers to access information or services. Servers function similarly to large data processing centers, handling multiple requests such as web browsing, data storage, and email responses. As a result, servers prioritize stability, security, and scalability over personal computers.
Servers require the cooperation between softwares and hardwares to conduct high performance computing (HPC). Hence, hardwares is installed with multiple motherboards to cope with professional needs, while softwares is designed to support multitasking and multiple users to handle simultaneous connections and multiple applications.
In the current market, servers can be categorized into three types based on their appearance.
| Pedestal Server | Rack Server | Blade Server | |
| Image |  |  |  |
| Size | Largest | Requires a server room | Requires a server room |
| Price | Lowest | Middle | Highest |
| Heat Dissipation | Good | Bad | Bad |
| Scalability | Good | Between | Bad |
| Ease of Management | Difficulties increase as server increases | Good | Good |
| Number of cables | Less | More | More |
| Performance | Bad | Between | Good |
| Maintenance | Difficult | Easy | Easy |
| Applicable firm | Firms with less demand for data computing and processing | Firms above certain scale | Data center, HPC, Cloud computing |
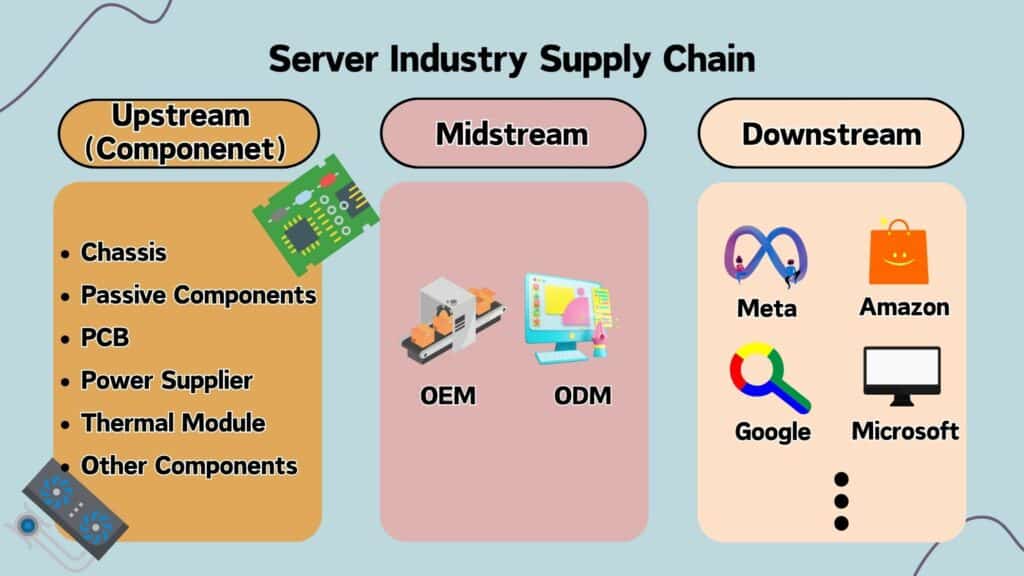
Taiwan has a sound supply chain for the server industry. In the upstream, Taiwan has many renowned electronic components suppliers, such as PSU (Power Supply Unit) supplier — Delta Electronics (2308.TW) and LITEON (2301.TW), Computer Chassis Manufacturer — InWin (6117.TW) and Chenbro (8210.TW), as well as PCB supplier — GCE (2368.TW) and Tripod-Tech (3044.TW). Moreover, with low defect loss, advanced R&D, and outstanding cost management, Taiwan EMS firms are popular for assembling AI servers worldwide. Based on data from Digitimes, over 90% of the world’s AI servers are assembled by Taiwan EMS firms.
In the current market, the server assembly process is primarily divided into 12 steps. Taiwanese EMS firms possess assembly capabilities at Level 6 or higher. As the assembly level increases, these firms earn higher revenue and profits. Below shows the difference between different levels.
| Level | Process | Firms |
| Level 1 | Collect and Manufacture of Server’s Electronic Components | |
| Level 2 | Assemble of Electronic Components | |
| Level 3 | Mount Electronic Components into computer chassis | |
| Level 4 | Mount power supply, flexible flat cable (FFC), and backplane to the end product of Level 3 | |
| Level 5 | Connect all of Level 4’s shell parts and IDE cable, as well as passing I/O tests | Chenbro, InWin |
| Level 6 | Integrate motherboard into the end product of Level 5 and conduct Power-on Self Test (POST). Products that pass the test are called Server Barebones. | Inventec, MiTAC, Wistron |
| Level 7 | Integrate Add-in Card into Server Barebones, and conduct POST | |
| Level 8 | Integrate hard drives into Server Barebones, and conduct POST | |
| Level 9 | Integrate CPU and Memories into Server Barebones, and conduct POST | |
| Level 10 | Complete the assembly of the server, including the testing of each component and the integration of the operating system. The delivery should be a perfectly integrated server with an instruction manual. | Quanta, Foxconn, Wistron, GIGABYTE |
| Level 11 | Build node connections between Level 10 servers, conduct testing, upload operating systems, and mount them into cable rack. | |
| Level 12 | Mount Level 11 racks together, and complete software loading, validation, and optimization for all networks. | Quanta, Foxconn, Wistron, Wiwynn, Super Micro, AMAX |
Simply put, the assembly process can be divided into three stages — The assembly of server barebones (Level 6), The assembly of a complete server (Level 10), and The integration of servers’ systems (Level 12). Currently, all of Taiwanese EMS firms possess Level 6 assembly capability, where some have even acquired Level 10 or Level 12 assembly capability.
In 2023, due to rapid advancements in AI technology and the success of ChatGPT, it was considered the “Year of AI”. Cloud service providers worldwide experienced a significant surge in demand for AI servers. In 2024, most enterprises increased their budgets for servers. Meta, for instance, plans to raise its 2024 annual capital expenditure to $33.4 billion, while Amazon anticipates capital expenditure to be significantly higher than the $48.1 billion in 2023.
AI servers are specifically designed for running machine learning and deep learning workloads. They prioritize data processing capabilities and the ability to perform fast matrix multiplications. Given the need for powerful computing performance, AI servers predominantly use chips that combine CPUs with GPUs or ASICs. Additionally, to meet the demands of intensive computation, AI servers typically feature high-spec components
Read More: The Robust Supporter Behind AI Servers – ASIC!
Regular servers are primarily used for data storage, executing applications, and providing network services. Their design emphasizes efficiency, stability, and reliable data storage. They excel in data transmission and control capabilities. However, relative to AI servers, regular servers rely mainly on CPUs for their functionality, resulting in comparatively weaker computing power. Additionally, most regular servers do not require high-spec electronic components. For instance, their power supplies typically range from 800W to 1200W, whereas AI servers utilize high-power supplies of up to 1800W.
| Regular Server | AI Server | |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Data Storage and Executing Applications | Enhance Computing Performance |
| Chips | Mainly focus on CPU, and partially focus on GPU | Mainly focus on GPU, and partially focus on CPU |
| Hard drives | Normally 5-10 SSD | Normally over 20 SSD |
| Memories | DDR4 | DDR5 |
| PCB | 8-10 layers of M6 boards | 14-16 layers of M6 boards or 18-20 layers of M8 boards |
| Power Supplier | 800-1200W | Over 1800W |
| Chassis | Normal Heat DissipationRely on fans | Excellent Heat DissipationRely on Liquid Cooling and fans |
| Cost | To enhance data storage, memories account for most of the cost. (Approximately 50%) | To enhance computing performance, GPU accounts for most of the cost. (Approximately 70%) |
The current shortage of AI chips, coupled with surging demand, has led to skyrocketing prices. High-spec electronic components used in AI servers led to higher costs. Additionally, during the assembly process, extensive human labor is required for compatibility testing of components. The “turn-key” method, which includes both labor and materials, aggregates all material and assembly testing costs. Consequently, AI servers costs are significantly higher than that of regular servers.
Furthermore, NVIDIA’s latest GB200 chip has a power consumption exceeding 1,000W. To tally with this, power supply specifications need to be upgraded, and the thermal dissipation limit (800-1,000W) must be surpassed. Liquid cooling technology, while optimizing efficiency, has also increased integration and testing complexity, further driving up costs.
| Amount in USD | 2*Intel Sapphire Rapids Server | Nvidia DGX H100 |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | 1,850 | 5,200 |
| 8GPU+4 NVSwitch Baseboard | – | 195,000 |
| Memory | 3,390 | 7,860 |
| Storage | 1,536 | 3,456 |
| SmartNIC | 654 | 10,908 |
| Chassis | 395 | 563 |
| Motherboard | 350 | 875 |
| Cooling | 275 | 463 |
| Power Supply | 300 | 1,200 |
| Assembly and Test | 495 | 1,485 |
| Markup | 689 | 42,000 |
| Total Cost | 10,474 | 269,010 |
Boost your industry Insights with TEJ Market Solution
Unveil All-encompassing Market data today!
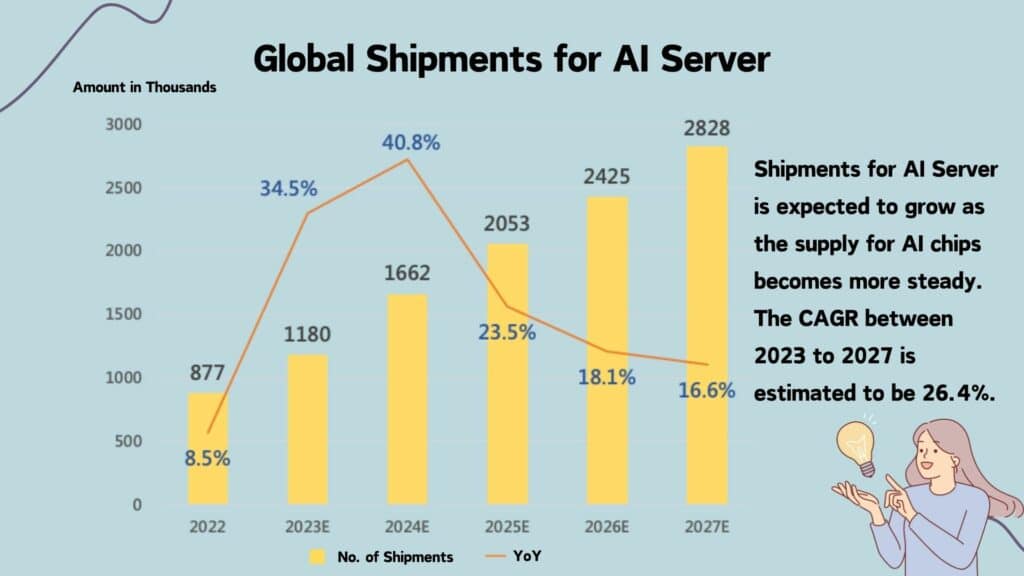
According to TrendForce’s research data, the annual shipment of AI servers in 2024 is expected to grow by 2.05% to reach 1.65 million units. With the continuous increase in AI chip shipments and the penetration of AI applications across various professional fields, other non-cloud vendors are also expected to follow suit. It is projected that from 2022 to 2027, the annual compound growth rate of AI server shipments will be 26.4%, resulting in a global shipment of 2.82 million units by 2027.
From the perspective of sales, based on Market.us data, AI server is expected to reach USD 430 billion, a CAGR of 30.3%, from 2023 to 2033.
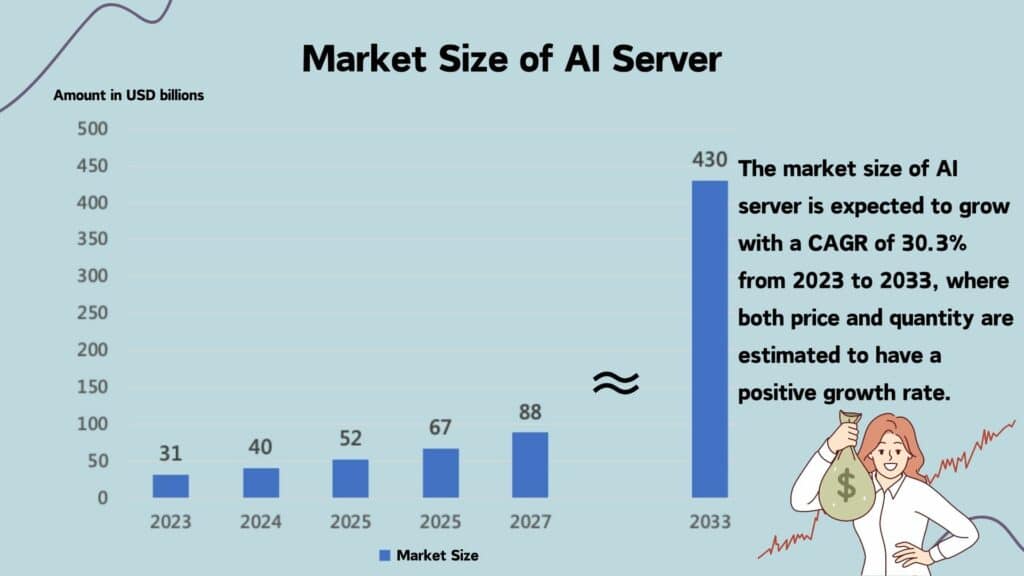
In summary, the rapid commercialization of generative AI has created a surge in demand for AI training. As a result, AI server shipments and sales are expected to grow by over 20% over the next five years.
At present, EMS firms primarily focus on 3C electronics products. To mitigate economic fluctuations and enhance growth momentum, many companies have diversified their business into non-consumer electronic products. Among these expansions, entering the server assembly market has been particularly popular. This trend is driven by the intricate safety regulations and certification procedures required for automotive and medical equipment, making entry barriers higher for these sectors. As a result, joining the server supply chain becomes comparatively easier. The chart below illustrates the revenue changes for major Taiwanese manufacturers with Level 12 production capabilities.
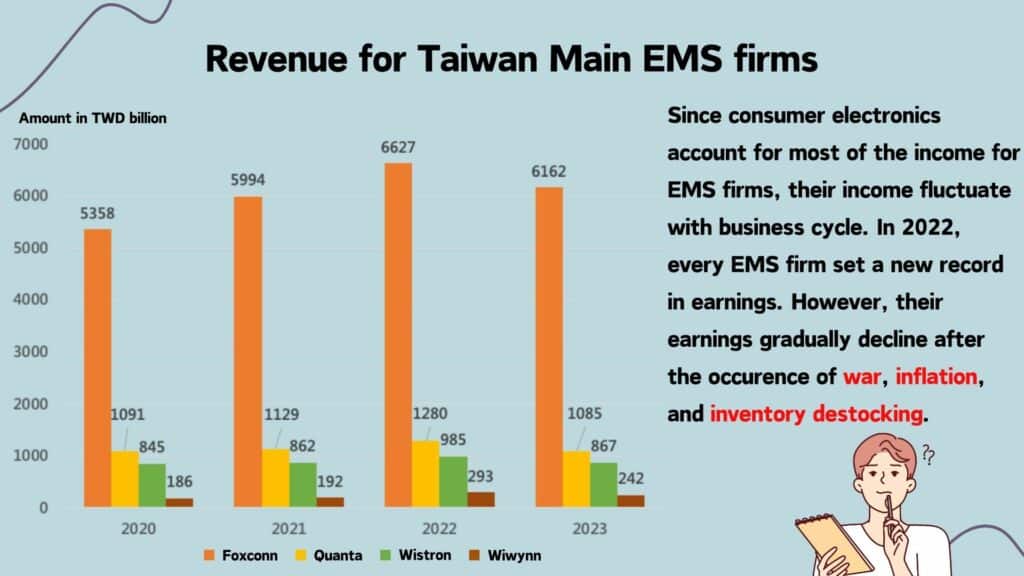
Foxconn (2337.TW) is a leading global contract manufacturer for server assembly. According to data from Digitimes, Foxconn holds an impressive 43% share of the global server manufacturing market, outpacing its closest competitor, Quanta, by approximately 26%. In recent years, Foxconn has gradually expanded into the field of AI server, primarily through its subsidiary, Ingrasys. Moreover, Ingrasys’ Taoyuan Nanying factory was recognized as the world’s first AI server lighthouse factory in 2023. Additionally, the company has become a major contract manufacturer for NVIDIA’s GB200 servers, displaying the GB200 NV72 server at Computex 2024. However, since Foxconn’s primary revenue source is still consumer electronics, the contribution of AI server revenue to the company’s overall profit margin remains relatively modest.
Quanta (2382.TW) is the world’s second-largest server assembly contractor, accounting for approximately 17% of the market share. Its primary focus is securing AI server project orders from the four major CSPs (Microsoft, Amazon, Google, and Meta). Currently, Quanta primarily offers Level 12 service. Starting in the third quarter of 2023, Quanta began mass-producing AI servers and also secured orders for NVIDIA’s latest GB200 servers. Despite a 15% decline in revenue in 2023, Quanta’s profit margin increased to 7.9% due to the higher shipment volume of AI servers. According to industry estimates, Quanta’s revenue share from AI servers is expected to reach 34% in 2024, further improving its profit margin performance.
Wistron (3231.TW) has currently secured orders for NVIDIA’s HGX Level 6 and DGX Level 10 servers. Additionally, Wistron has obtained orders for the new generation AMD MI300 series AI server boards. Apart from serving the four major CSPs, the company has also secured AI server orders from other non-cloud vendors. Although Wistron experienced a decline in revenue in 2023, the increased shipment volume of AI servers led to a rise in the company’s profit margin to 8.6%. Furthermore, Wistron has also received orders for partial assembly of the latest GB200 MGX servers, indicating an expected continued increase in the company’s revenue share from AI servers and a sustained improvement in profit margins in 2024.
Wiwynn (6669.TW) primarily provides hardware and solutions for large-scale cloud data centers. Its current revenue mainly comes from full rack server shipments. The company’s downstream customers are primarily CSPs (Cloud Service Providers), and Wiwynn has also secured orders for NVIDIA’s latest GB200 servers. Despite a decline in revenue in 2023, Wiwynn’s profit margin significantly increased to 9.8% due to higher shipment volumes of AI servers.
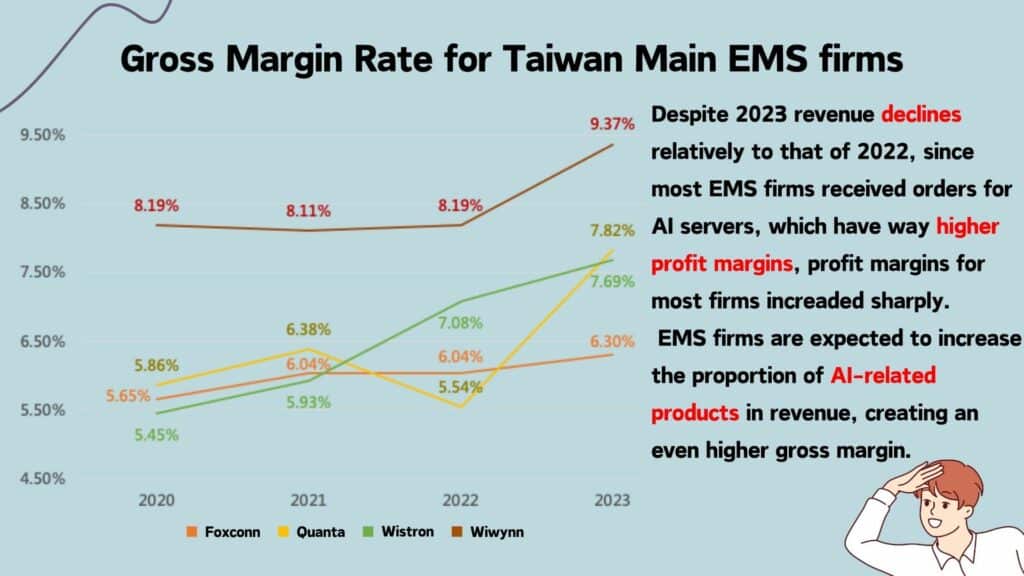
Based on the above, despite the decline in revenue, benefiting from the change in structure of revenue,EMS firms with AI servers accounting for a high portion of revenue attained a higher gross margin rate in 2023.
With this year’s theme being “Connecting AI”, 2024 Computex gathered leading tech companies displaying their breakthroughs in AI. Ingrasys and Inventec presented the full rack of GB200 servers, where Delta Electronics, Chenbro, and InWin released their corresponding components. By virtue of past experiences, Taiwan EMS firms made profit through catching the AI trend, despite the weakened demand in consumer electronics. Besides cloud AI, edge AI is also highly anticipated. If successfully implemented, it will continue to drive device specification upgrades and increase profits for EMS firms.
Boost your industry Insights with TEJ Market Solution
Unveil All-encompassing Market data today!
Read More: The Protector for all Electronic Products – Passive Component