
Table of Contents
ESG stands for “Environmental, Social, and Governance”, whereas ESG data essentially means the information that reflects a company’s performance in these three areas. This data can be used to assess a company’s commitment to sustainability and social ethics, serving as a framework for investors, analysts, companies, policymakers, or other stakeholders to make responsible investment and well-informed financial decisions.
Environmental data measures the amount of energy used by a company and the overall positive or negative environmental impact caused by this usage. ESG data examples in this category include greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, water usage, and waste generation.
This type of ESG data focuses on a company’s relationships with its employees, communities, and stakeholders, which can be determined through factors like labor practices, human rights policies, community engagement, as well as diversity and inclusion initiatives.
Governance data examines a company’s internal structure and management policies. It includes aspects like board composition, executive compensation, anti-corruption policies, and the presence of any internal conflicts.
Based on findings of industry reports (e.g. those from established firms like Morgan Stanley and Borsta Istanbul) and academic research, ESG data offers various benefits for stakeholders. It doesn’t just help companies address environmental and ethical concerns that affect operations and reputation, but also raises the chance of better financial returns, while lowering risks. Thus, stakeholders are looking beyond the financial performance of companies.
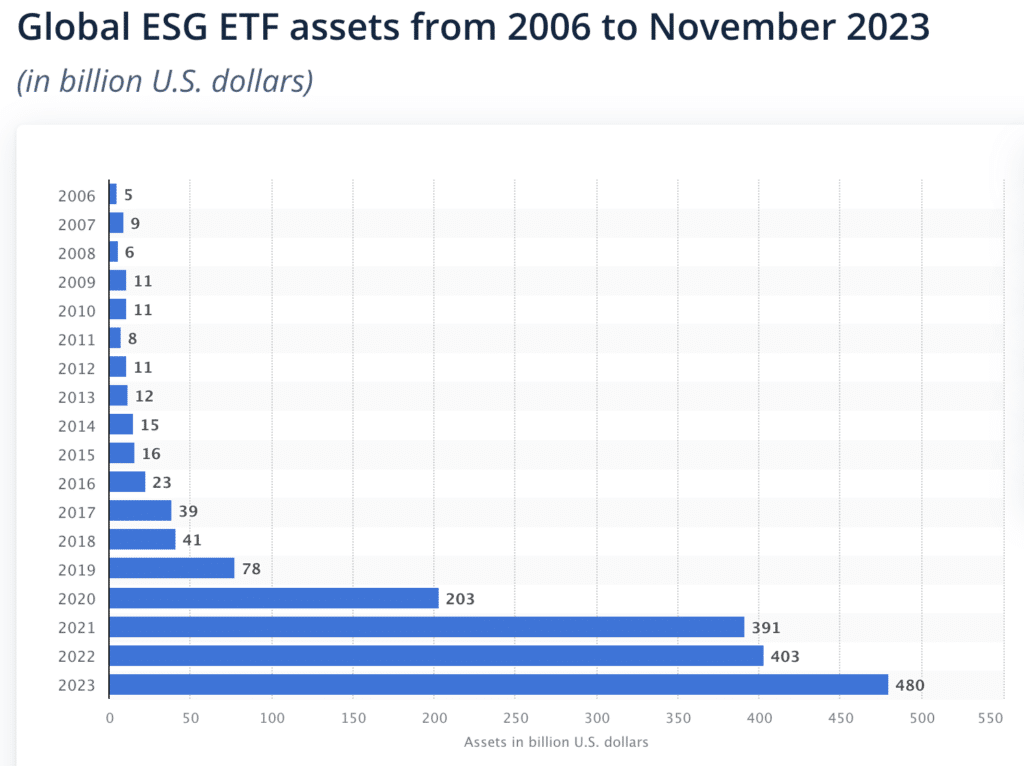
Source: Statista
As of 2023, up to $480 billion exchange-traded funds (ETF) have been allocated to companies that implement ESG strategies, which is a 22.76% increase from the $391 billion figure in 2021, reflecting the growing focus on environmental and social responsibilities in the financial landscape. With this in mind, the benefits of leveraging ESG data will be discussed further in the next section.
While both ESG and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) aim to make businesses more responsible, they differ significantly in their approach and application. CSR, traditionally, has been about a company’s self-regulated efforts to have a positive impact on society. It’s often driven by a company’s values and a desire to be a good corporate citizen, encompassing activities like reducing carbon emissions, engaging in philanthropy, and improving labor practices. For example, a company might donate 1% of its annual profit to a local charity, which is a CSR action. However, these initiatives can vary widely and lack standardized metrics for measuring their impact.
In contrast, ESG provides a more structured and measurable framework – environmental impact, social responsibility, and corporate governance – with quantifiable metrics that investors and stakeholders can use to evaluate a company. The company may use CSR to form its internal mission and values while using ESG to set measurable goals that are public-facing and tracked by investors and stakeholders.
The investment landscape is evolving beyond traditional financial returns, with a growing emphasis on how businesses affect the environment and society. This shift has led to a surge in values-based investing strategies, including ESG investing, Socially Responsible Investing (SRI), and Impact Investing. While these approaches share common ground, they differ significantly in their objectives and how they influence investment decisions. Understanding these distinctions is critical for both investors and companies.
ESG integrates environmental, social, and governance factors into financial analysis. It seeks to identify companies that are well-managed and sustainable since these signs often lead to better long-term financial performance, as seen in a 2023 study by the Morgan Stanley Institute for Sustainable Investing.
It builds upon ESG by incorporating ethical guidelines and aligning investment decisions with a specific set of values. This often excludes certain sectors or industries, such as tobacco, firearms, or fossil fuels. A 2020 report by the Global Sustainable Investment Alliance found that SRI strategies accounted for nearly $35.3 trillion in assets globally, with an increasing number of investors focusing on companies with a positive social impact. However, SRI’s exclusion-based approach might limit diversification and potentially reduce returns compared to broader market indexes. For instance, a fund that excludes oil and gas companies will have limited exposure to the energy sector, which could be positive or negative depending on market conditions.
This takes the values-based approach, focusing on generating positive social or environmental change and a financial return. It prioritizes measurable impact over financial returns, seeking investments that actively address societal challenges such as poverty, climate change, or health care access. While impact investments may have higher risks, particularly in emerging markets, and potentially lower liquidity, they attract investors who seek to align their capital with a clear mission.
ESG data is crucial for modern businesses due to increasing stakeholder demand for transparency. Consumers, employees, and investors seek companies with strong sustainability, diversity, and ethical practices by analyzing ESG data.
Moreover, new regulations like the EU’s CSRD mandate ESG disclosures. Thus, ESG data reporting is essential for demonstrating corporate responsibility, attracting talent, securing investment, and complying with evolving legal frameworks. A robust ESG database provides the information needed to not only attract top talent and secure investment but also ensure compliance with evolving legal frameworks. Therefore, the question is no longer if you need ESG data, but how to effectively use an ESG database to gain actionable insights.
By acknowledging the potential inaccuracy and bias of internal ESG data, companies must establish a robust data collection process that incorporates external verification and standardized metrics. This ensures that they gather reliable information that reflects their sustainability efforts and allows strategic decision-making. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps involved:
The first step is to define the company’s ESG goals and priorities. Consider the environmental and social issues most relevant to your industry and operations. You should also identify the needs and expectations of stakeholders, such as investors and customers. This ensures that the collected data is relevant and actionable.
Frameworks like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) provide standardized metrics for ESG reporting. By choosing a framework, you obtain a clear structure for data collection, ensuring comparability and consistency with industry standards.Here’s a breakdown of common elements and popular frameworks.
Common ESG Elements:
Popular Reporting Frameworks:
As mentioned earlier, you should consider combining data from both internal and external sources. Internal data can refer to the information disclosed in a company’s sustainability report. Externally, industry benchmarks, ESG ratings, weather patterns, and public perception are key. This data can then be supplemented with information from reputable sources like public ESG datasets and specialized ESG data providers, which can help you offer a more comprehensive ESG data for analysis. TEJ provides a complete set of tools and information for ESG, based on more than 20 years of research. We offer a TESG Rating and special data for green and sustainable investments, making them a single place to get all your ESG information.
Develop a clear and efficient process for collecting data from various sources. This may involve creating standardized data collection forms, utilizing data management software, and designating specific teams responsible for gathering information. It is also important to implement a secure data storage system to ensure data integrity and accessibility for analysis or reporting.
TEJ exemplifies this approach in our ESG data compilation process, gathering company disclosures from sources like MOPS, company websites, financial reports, shareholder reports, and external sources including the Ministry of Environment and the Ministry of Labor. This ensures the collection of relevant and publicly available ESG information.
To further maintain data integrity, we keep source versions and the historical data trail in the data warehouse, guaranteeing consistent data definitions for accurate ESG data and analysis.
Understanding ESG data is crucial for investors and bankers seeking to evaluate a company’s sustainability performance. This involves navigating various metrics, including ESG scores, risk ratings, and impact ratings while considering the differences between qualitative and quantitative data.
When analyzing ESG data, it is essential to distinguish between qualitative and quantitative data. Quantitative data is measurable and numbers-based, such as a company’s carbon emissions, the number of women on the board, or the number of workplace accidents. Qualitative data, on the other hand, provides context and interpretation, describing the reasons behind numerical changes or the quality of relationships with stakeholders. For instance, a company can report the quantitative figure of a 10% decrease in water usage. Consequently, qualitative data could explain the improvements to water management that brought about such improvement.
Once data is collected and validated, analyze it to identify trends, track progress towards ESG goals, and uncover areas for improvement. This data-driven approach allows companies to make informed decisions regarding sustainability initiatives and resource allocation.
The key to effective ESG lies in analyzing validated data to set firm guidelines for judging strengths and weaknesses in a company’s ESG performance. This approach identifies key trends, tracks progress toward sustainability goals, and informs smart investment and lending choices. Armed with these insights, craft comprehensive ESG reports—aligned with recognized frameworks—that highlight a company’s commitment to sustainable development goals and make a case for investment to stakeholders. By being transparent with what a company can excel at and areas needing improvement, this strategic use of ESG data effectively guides investment toward positive societal impact, turning ethical practices into a driver of long-term financial success.
ESG data collection and reporting is a long-term effort. Regularly review and update the ESG data itself to make sure it remains relevant and accurate. The collection procedures and reporting frameworks should be reviewed as well. This is to ensure they remain effective and aligned with the stakeholder expectations and industry standards that are constantly evolving.
ESG data offers a multitude of benefits for companies, investors, and stakeholders alike. By leveraging this data, organizations can gain valuable insights that lead to improved decision-making, risk reduction, and a more sustainable future.
Navigating complex environmental and social regulations can be challenging. ESG data helps companies stay ahead of regulatory requirements on responsible investment or responsible finance to reflect their commitment to ethical practices while avoiding legal repercussions and financial penalties.
Transparency is key to building a strong reputation. ESG data allows companies to openly share their sustainability and social responsibility efforts, which can help them gain the trust of consumers and investors, thereby significantly enhancing their brand image and market position.
For example, a 2019 study by Unilever found that 33% of consumers are willing to pay more for sustainable brands. However, several major brands have been heavily criticized for greenwashing as they make unsubstantiated claims about their sustainability practices. A survey conducted by KPMG has even shown that 54% of the consumers responded that they would stop buying products from a company with misleading sustainability claims, while 38% of the respondents say that they would stop their investments with such companies. This highlights the importance of backing up ESG claims with verifiable data, which can help companies build trust and avoid reputational damage.
Another major benefit of ESG data is how it can empower companies to identify and address potential environmental or social risks before they escalate. Currently, 54% of companies worldwide implement ESG strategies for risk inventory reporting. In turn, this proactive approach helps the company’s investment and credit strategies avoid potential investment risks.
For instance, the California Transparency in Supply Chain Act (SB 657) requires large retailers and manufacturers operating in California to disclose their efforts in eradicating slavery and human trafficking from their supply chains. By leveraging ESG data to track and monitor labor practices within their supply chains, companies can proactively identify and address potential human rights violations. Not only will this minimize legal risks, but also prevent financial loss from consumer boycotts.
ESG data offers metrics to let companies align their strategies with long-term goals. This data-driven approach will then contribute to sustainable growth and performance.
For example, a manufacturing company can analyze its ESG data to identify areas of high energy consumption. By implementing energy-efficient practices based on this analysis, the company can lower energy costs, leading to better profit in the long run. Reports by McKinsey & Company have even indicated an enterprise, such as 3M, has saved up to $2.2 billion since they began their sustainability program to boost waste reduction and recycling efforts, reflecting the positive impact of ESG strategies.
For investors, ESG data serves as a reliable criterion that provides a deeper understanding of a company’s ethical and sustainable practices. This enables investors to choose companies that align with their values, leading to more socially responsible investments.
For instance, an investor considering companies in the energy sector can use ESG data to assess their carbon footprint reduction strategies and investments in renewable energy sources. This is especially crucial if the investor is considering expanding to Europe, as the European Union’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and Sustainable Products Regulation require listed companies to publish reports on their social and environmental efforts. With ESG data, the investor can determine if the company aligns with their sustainability goals and future development plans.
Research, such as the ones published in the Journal of Business and Management and the Academic Journal of Management and Social Sciences, have indicated a positive impact of ESG ratings on employee employment and performance. Moreover, a survey conducted by KPMG has revealed that 46% of workers want their companies to display a commitment to ESG, while 20% of these workers have even refused job offers when the companies’ ESG strategies do not align with their own values. This shows that companies prioritizing ESG metrics often attract top talent, as employees are more likely to join and stay with companies that have strong social and environmental values.
Furthermore, a study by Gallup found that companies with highly engaged workforces experience 23% higher profitability. This is something companies can enhance with ESG data. For example, if a company with a high employee turnover rate analyzes their ESG data, they may find its correlation between low employee engagement scores and lack of investment in employee wellness programs. The company can then allocate resources to improve employee well-being, leading to higher retention and increased productivity, as well as improved financial performance.
While ESG data offers significant advantages, there are challenges to consider, particularly regarding data accuracy and potential bias. This is because internal ESG data collection may be susceptible to unintentional errors or inconsistencies. Additionally, companies that prioritize presenting themselves in a positive light might even choose to conduct data manipulation or selective reporting. Consequently, this may mislead stakeholders and consumers.
To combat this issue, it is recommended to complement internal data with information from external sources like public ESG datasets or specialized ESG data providers. These third-party providers can offer a more objective perspective, as they gather data from various sources, including company reports, sustainability ratings, and news articles, helping to minimize bias, while adding credibility and accuracy to a company’s ESG reports.
The landscape of ESG reporting is transforming, moving beyond the politicized term “ESG” to focus on underlying issues of long-term value creation. Here’s a look at the key trends shaping the future of how companies will communicate their sustainability efforts:
Companies use several reports in addition to ESG to showcase their commitment to sustainability and ethics. These reports provide deeper insights into specific areas of corporate responsibility.
In the modern investment landscape, ESG data is more than a trend, it is a vital tool for sustainable and ethical business practices. By understanding and leveraging ESG data, businesses can analyze their ESG performance and develop effective strategies. At the same, financial stakeholders, such as investors and data analysts, can also make more informed decisions that contribute to long-term success.
As a leading ESG data provider in Taiwan, TEJ delivers accurate and detailed information verified by international standards like SASB. Our cutting-edge technology and expert analysts power a full suite of ESG data solutions, including datasets, a Rating Index, and a real-time ESG Event Radar. With over 40 variables and 600 subjects, TEJ’s database ensures comprehensive analysis, even without full CSR reports, overcoming the issue of incomplete disclosures.
Furthermore, our team of experts, including ESG-carbon managers and ESG certification holders, provides valuable guidance to help you translate data into actionable insights for your business. Learn more about our ESG solutions, alternative data, market data, quantitative strategy, analysis model, long-short equity strategy, and event-driven investing to take your data strategy to the next level.